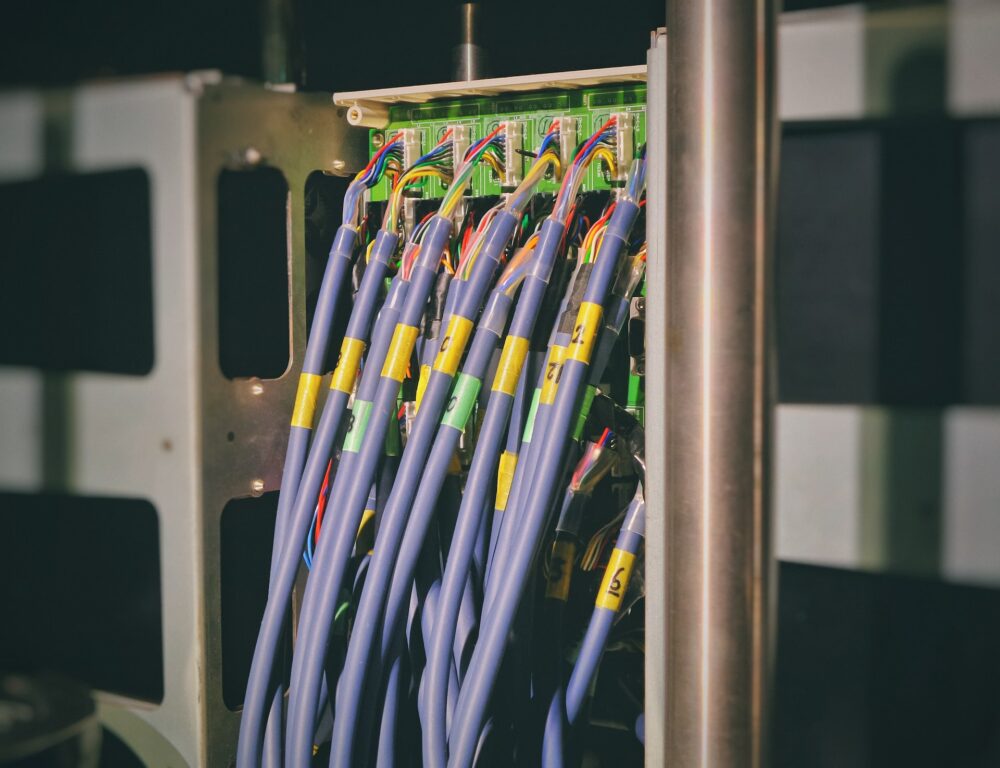
The Ontario and Canadian governments have agreed to a collaborative effort to connect 19,000 homes in over 47 underserved communities to high-speed broadband internet.
Friday’s announcement from Innovation, Science And Economic Development Canada includes over $109 million in combined funding spread between two distinct funding directions. These are likewise separated into $61 million for six projects by Bell Canada, the Thunder Bay-based nonprofit Northwestern Ontario Innovation Centre and the Keewaytinook Okinmakanak northern chiefs council.
Subsequently, the second announcement was for $48 million for a project by YorkNet, a corporation owned by the Municipality of York. This would bring high speed internet access to over 3,800 homes in 31 Ontario communities.
The projects are part of an earlier partnership between the two governments. On July, 2021, the governments announced a Canada-Ontario broadband partnership to support large-scale, fibre-based projects. These projects would provide high-speed internet access to over 280,000 residential and commercial clients across the province. The agreement came about courtesy of a joint $1.2 billion federal-provincial investment.
“Having fast, reliable Internet helps rural Canadians by levelling the playing field to access essential services like health care and education, participate in the digital economy, or simply connect with loved ones,” said Gudie Hutchings, Minister of Rural Economic Development in a statement.
Read more: Competition Tribunal rules in favour of Rogers and Shaw telecommunications merger
Read more: The Mugglehead technology roundup: telecommunications and media concentration edition
Government of Canada wants 100 per cent broadband internet connectivity by 2030
The Canadian government’s has a stated goal of getting 98 per cent of Canadians internet access by 2026.
The government also has a stretch goal of 100 per cent connectivity by 2030.
One of the government’s first steps included Ontario’s passage of the Supporting Broadband and Infrastructure Expansion Act, 2021 for high-speed internet projects. They then subsequently followed up with the Getting Ontario Connected Act, 2022 to further reduce barriers, delays and duplication.
Additionally, the government isn’t approaching this issue alone, either. Various internet service providers have partnered with it to install the required infrastructure to connect their communities.
These providers include Bell Canada and Celerity Telecom, which is working with the Northwestern Ontario Innovation Centre.
Follow Joseph Morton on Twitter
joseph@mugglehead.com