While scientific research on cannabis has focused mostly on the multitude of compounds found in the budding part of the plant, a new study is rooting out therapeutic benefits from source with less visibility.
The aqueous extract derived from the roots of a pot plant — of which cannabissativine (CsAqEx) is the main component — presents anti-inflammatory activity in mice without noticeable negative side effects or toxicity, according to a study published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology.
Specifically, researchers found CsAqEx is associated with the reduction of vascular extravasation — the leakage of blood or other fluids from a blood vessel or tube — and the migration of inflammatory cells, which help reduce inflammation at affected sites. No effects to the central nervous system were observed, and there was no spasmolytic effect — the contraction of soft tissues — in airways.
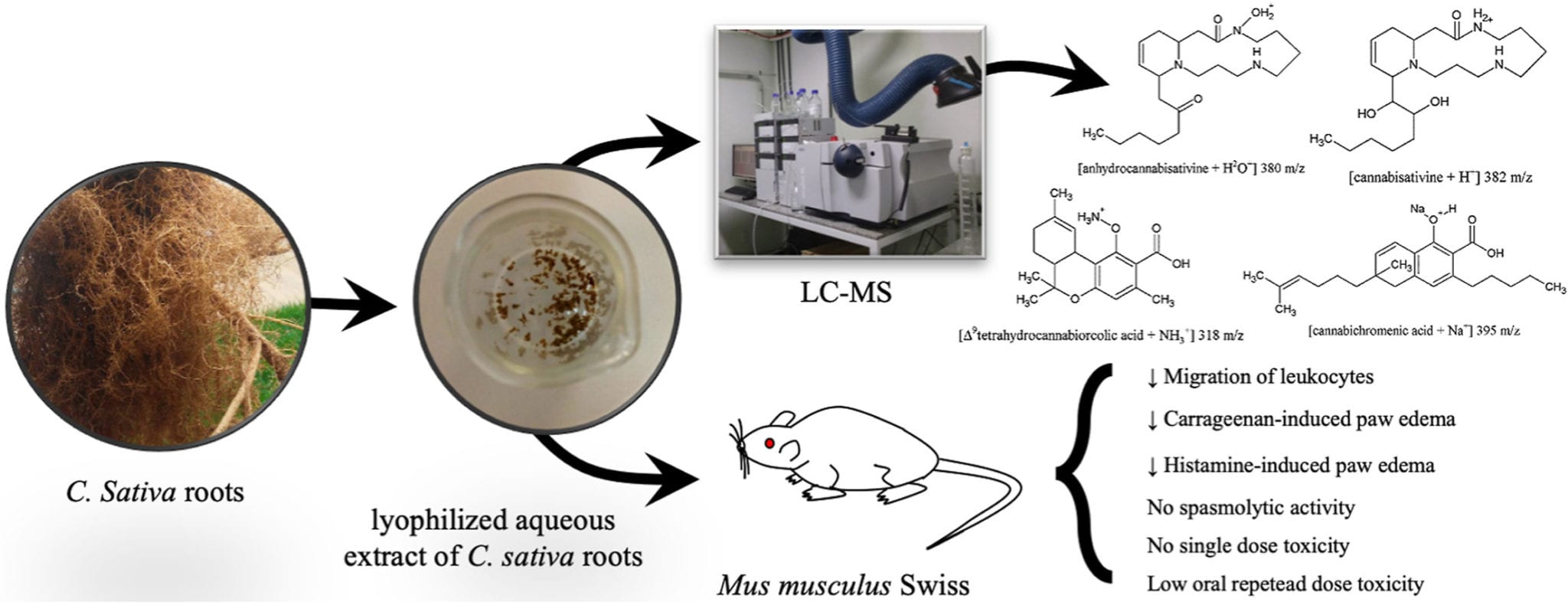
Image via “Cannabis roots: pharmacological and toxicological studies in mice”
The results suggest that the anti-inflammatory effect of CsAqEx is related to the reduction of vascular extravasation and migration of inflammatory cells, without effects on the central nervous system. Moreover, there was no spasmolytic effect on airway smooth muscle and no toxicity was observed on mice.
Read more: Martha Stewart and Canopy Growth release CBD dog treats — but are they safe?
Read more: Giving dogs daily CBD improves arthritis symptoms: study
The researchers assessed the root compound’s effectiveness by causing inflammation in mice. In technical terms, with carrageenan-induced leukocyte migration assay, and carrageenan and histamine-induced paw edema methods.
They found that CsAqEx inhibited the migration of leukocytes at the doses of 25, 50, and 100 milligrams per kilogram. CsAqEx also showed anti-inflammatory activity after the injection of carrageenan into the mice’s paws, presenting a reduction in swelling at all tested doses, the lowest being 12.5 milligrams per kilogram.
Airway contraction was tested with isolated mice trachea in vitro. In an organ bath, 729 micrograms per millilitre of CsAqEx didn’t produce spasmolytic effect on isolated tracheal rings contracted by carbachol (CCh) or potassium chloride (KCl).
No negative impact on motor function was observed, which was tested using rotarod and open field tests.
Researchers found no toxic effects from single-dose tests of 1,000 milligrams per kilogram, nor from repeated doses of 25 or 100 milligrams per kilogram over 28 days.
The root compound didn’t produce any other significant changes to to the mice’s organs.
Cannabis roots have a long history of medical use, but their therapeutic applications have been largely ignored in the modern age.
Top image via iStock
nick@mugglehead.com