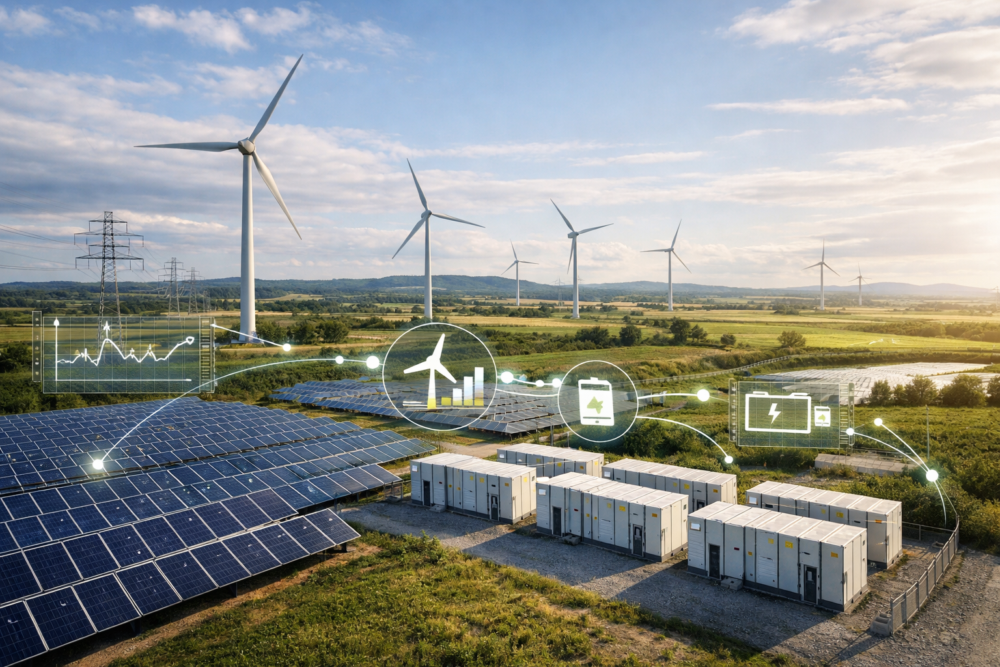
The artificial intelligence market tied to renewable energy is moving from niche experiments to core infrastructure, as power systems grow more complex and data driven.
According to a new report from Allied Market Research, the artificial intelligence in renewable energy market reached USD$0.6 billion in 2022 and is projected to climb to USD$4.6 billion by 2032. The firm expects the sector to expand at a compound annual growth rate of 23.2 per cent between 2023 and 2032, driven by rapid global deployment of clean power and smarter grids.
The growth reflects rising use of AI tools that help operators predict output, manage equipment, and stabilize power networks. As governments push for lower carbon emissions, renewable energy producers face pressure to deliver consistent electricity from variable sources. Consequently, developers increasingly rely on algorithms that process weather data, grid signals, and equipment performance in real time.
Artificial intelligence now plays a central role in making solar and wind power more dependable. These technologies allow renewable assets to operate closer to their maximum potential. Additionally, AI systems reduce costs by cutting downtime and improving planning across energy networks.
Asia-Pacific emerged as both the largest revenue contributor and the fastest-growing region in 2022. Rapid solar and wind deployment continues across China, India, and Japan, supported by national clean energy policies. Furthermore, governments across the region invest heavily in smart grid infrastructure, which creates fertile ground for AI-based energy tools.
China continues to install renewable capacity at an unmatched pace, while India accelerates solar projects to meet rising electricity demand. Meanwhile, Japan focuses on grid resilience and storage integration following years of energy reform.
Read more: New AI model allows farm robots to identify and kill unfamiliar weeds instantly
Read more: Rupert Murdoch’s media conglomerate employs tech startup Symbolic.ai for journalism help
Solar energy clearest use case for AI
North America also shows strong momentum, particularly in distributed energy management. According to data from the International Renewable Energy Agency, the United States installed more than 111 gigawatts of solar photovoltaic capacity in 2022, up from 93.91 gigawatts a year earlier.
That expansion increases the need for software that can balance thousands of small generation points. Consequently, utilities and developers adopt AI to manage rooftop solar, batteries, and local grids.
Solar energy applications represent one of the clearest use cases for artificial intelligence. In photovoltaic systems, AI models analyze weather forecasts, track cloud movement, and calculate optimal panel positioning.
Additionally, automated systems adjust orientation and output settings throughout the day to capture more sunlight. These improvements raise overall energy yield without expanding physical infrastructure.
AI tools also help solar operators predict maintenance needs before faults disrupt production. By detecting subtle changes in performance data, algorithms flag potential issues early. Subsequently, technicians can fix problems during scheduled maintenance rather than emergency shutdowns.
Wind power operators follow a similar path. AI systems forecast wind patterns hours or days ahead, helping grid managers plan supply. Furthermore, machine learning tools monitor vibration, temperature, and acoustic data from turbines to identify early signs of mechanical stress. Predictive maintenance reduces downtime and extends equipment life, improving project economics.
As renewable assets become more efficient, investors view them as lower-risk infrastructure. Consequently, capital flows toward projects that integrate advanced analytics and automation. That shift further accelerates adoption of AI across the renewable energy value chain.
Read more: Fusemachines stock soars on AI collaboration with IBM partner modulAIre
Read more: Google Research discovers that repeating LLM prompts twice gives superior answers
Grid optimization strong strategic application for AI
Energy storage represents another major growth opportunity. Batteries help smooth the mismatch between renewable generation and electricity demand. However, storage systems require careful management to maximize value. AI platforms analyze production patterns, consumption trends, and price signals to decide when to charge or discharge batteries. Additionally, these systems respond instantly to grid conditions, supporting stability during peak demand.
By storing excess renewable energy and releasing it later, AI-managed batteries improve overall system efficiency. In addition, they help utilities avoid costly grid upgrades by reducing congestion. As renewable penetration rises, such intelligent storage solutions become essential rather than optional.
Grid optimization remains one of the most strategic applications of artificial intelligence. Traditional grids were designed for predictable, centralized power plants. Renewable energy introduces variability and decentralization. Consequently, operators turn to AI to forecast demand, balance supply from multiple sources, and route electricity efficiently.
AI-driven grid platforms analyze massive volumes of sensor data from substations, lines, and meters. Furthermore, they adjust power flows in real time to prevent overloads and outages. These capabilities support higher renewable shares without sacrificing reliability.
Beyond generation and grids, artificial intelligence improves energy efficiency in buildings and industry. Smart thermostats, lighting systems, and appliances learn user habits and adjust consumption automatically. Additionally, these systems shift energy use away from peak periods, reducing strain on the grid.
In factories, AI-powered monitoring detects inefficiencies and equipment issues that waste energy. Predictive maintenance systems prevent unexpected failures and reduce losses. Consequently, companies cut costs while supporting broader clean energy goals.
Read more: Onslaught of junk AI content prompts Merriam-Webster to select ‘slop’ as its word of the year
Read more: McDonald’s pulls Grinchy AI-made Christmas ad after avalanche of complaints
Software platforms dominate current deployments
Environmental considerations also shape AI deployment in renewable energy. Poorly planned projects can disrupt ecosystems and wildlife. However, AI models help developers choose locations and operating strategies that reduce harm. For example, algorithms can predict bird migration patterns and adjust wind turbine activity accordingly. Additionally, such tools help minimize land use and carbon footprints across project lifecycles.
The artificial intelligence in renewable energy market includes several deployment models. On-premises systems attract interest because they offer strong data security and low latency. Meanwhile, cloud-based platforms remain popular for their scalability and lower upfront costs. The balance between these approaches depends on regulatory requirements and operational needs.
The market also divides into solutions and services. Software platforms dominate current deployments. However, the services segment grows quickly as utilities seek help with integration, customization, and long-term support. Consequently, consulting and managed services become a key revenue stream for technology providers.
By end-use, energy distribution stands out as a high-growth segment. Utilities increasingly deploy AI to manage load balancing, detect faults, and coordinate distributed resources. Additionally, these tools support real-time decision making as grids grow more complex.
Technology advances continue to push the market forward. AI algorithms improve forecasting accuracy and reduce electricity waste. Furthermore, real-time analytics allow operators to respond instantly to changing conditions. These features prove critical as renewable energy supplies a larger share of global electricity.
Several major companies compete in this evolving landscape. General Electric (NYSE: GE) develops AI-enabled grid and generation technologies. Siemens AG (OTCMKTS: SIEGY) integrates artificial intelligence into power flow control and grid automation.
Read more: Wonder Studios raises US$12M in seed for AI film production
Read more: AI brings Wizard of Oz to life like never before in Las Vegas
Partnerships between utilities and firms expanding
In addition, Enphase Energy (NASDAQ: ENPH) focuses on AI-driven solar and storage management. ATOS SE (EPA: ATO) provides digital platforms for energy optimization. Flex Ltd. (NASDAQ: FLEX) supports smart energy systems through advanced manufacturing and analytics.
Other participants include Alpiq, AppOrchid, Enel Green Power, and Origami Energy, which emphasize software, integration, and grid services. Meanwhile, partnerships between utilities and technology firms continue to expand, as both sides seek faster deployment and proven results.
As renewable energy systems scale globally, artificial intelligence increasingly acts as the connective tissue that keeps them reliable, efficient, and economically viable.
.