IonQ, Inc. (NYSE: IONQ) has signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) with the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) to accelerate the development of quantum technologies in space.
Announced Thursday, the agreement supports the DOE’s growing Quantum in Space (QIS) initiative and outlines IonQ’s role in demonstrating quantum ground-to-orbit-to-ground capabilities.
Under the MOU, IonQ will design and execute an orbital demonstration of quantum-secure communications using its satellite platform. The collaboration will also explore additional quantum applications in space, including advanced position, navigation, and timing (PNT) systems, time synchronization, quantum networking, and sensing. Furthermore, the partnership will lay the groundwork for testing quantum algorithms and potentially deploying quantum computing on satellites.
“By working alongside the DOE, we aim to demonstrate the power of quantum computing and networking for secure communications,” said Niccolo de Masi, Chairman and CEO of IonQ.
“This MOU reflects the growing importance of quantum technologies in achieving global leadership in space innovation and cybersecurity.”
The MOU provides a framework for demonstrating a broad range of quantum capabilities in orbit. Initially, IonQ will focus on demonstrating quantum-secure networking through its satellite assets.
“By bringing in new partners, we are accelerating commercialization and demonstrating applications like secure quantum communications, advanced quantum PNT, and quantum sensing,” said Rima Kasia Oueid, DOE Senior Commercialization Executive and lead architect of the Quantum-in-Space Collaboration.
“Additionally, this collaboration will expand America’s role in the space economy. It will help us seed a quantum sandbox in space to support resource exploration and the manufacturing of high-value products.”
Read more: IonQ inks research deal with United States Air Force for quantum computing
Read more: Arqit Quantum shares bounce 25% after 25:1 stock split
Quantum computers harness principles of quantum mechanics
Quantum computing is an advanced field that leverages the principles of quantum mechanics to process information in fundamentally new ways.
Unlike classical computers that use bits as the smallest unit of data, quantum computers utilize qubits, which can exist in multiple states simultaneously due to superposition. This capability allows quantum computers to perform certain calculations exponentially faster than classical systems.
Additionally, quantum entanglement enables qubits to be interconnected, facilitating complex problem-solving.
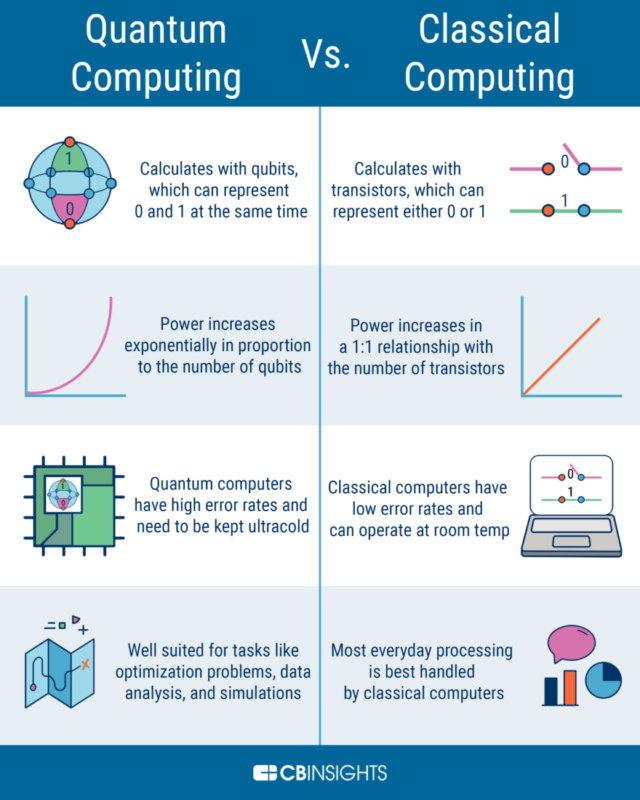
Image via CBInsights.
According to the U.S. Department of Energy, quantum computers are designed to harness the principles of quantum mechanics, enabling them to solve complex problems more efficiently than classical computers. By manipulating quantum bits (qubits), these computers can process information in ways that classical computers cannot, potentially transforming fields such as cryptography, optimization, and drug discovery.
While still in the developmental stage, quantum computing holds the potential to revolutionize industries such as cryptography, materials science, and artificial intelligence by solving problems that are currently intractable for classical computers.
IonQ also acquired quantum networking pioneer Qubitekk in late 2024 and space technology company Capella in 2025.
The company currently delivers commercial quantum networking systems. Further, these including installations with the U.S. Air Force Research Laboratory and the EPB Quantum CenterSM in Chattanooga, Tennessee.
Consequently, the company positions itself as the only U.S. quantum computing firm actively integrating space-based quantum technologies with real-world applications.
IonQ’s current-generation quantum computers, IonQ Forte and IonQ Forte Enterprise, offer high-performance systems designed to solve complex problems. In addition, partners such as Amazon Web Services, AstraZeneca plc (NASDAQ: AZN), and NVIDIA Corp (NASDAQ: NVDA) (ETR: NVD) have reported up to 20x performance improvements using IonQ systems.
.